District Health Information System 2 (DHIS2)
District Health Information Software 2 (DHIS2) is a free and open source health management data platform used by multiple organizations, including the European Union (EU), and governments worldwide. A total of 54 countries are deploying DHIS2 on a national scale, 30 of which are in the pilot stage or early phase in their rollouts. Since DHIS2's release in 2006, NGOs and national governments in 60 countries have deployed DHIS2 for health-related projects, including patient health monitoring, improving disease surveillance and pinpointing outbreaks, and speeding up health data access.
DHIS2 is an open source software platform developed by the Health Information Systems Program (HISP) and supported by the University of Oslo's Department of Informatics. Although HISP initially focused on grassroots health committees and Community Information Systems in South African health districts, DHIS was quickly adopted for national implementation by South Africa and other African countries as was the web-based version, DHIS2, after its development in 2005-2006.
DHIS2 is used to aggregate statistical data collection, validation, analysis, management, and presentation. This data analytics and management platform is completely web-based and boasts great visualization features and the ability to create analysis from live data in seconds. In addition, DHIS2 can be used to monitor patient health, improve disease surveillance, map disease outbreaks, and speed up health data access for health facilities and government organizations.
The user interface of DHIS2 has been fully translated into eight languages: English, Chinese, Spanish, French, Russian, Portuguese, Vietnamese, and Tajik. DHIS2 also allows users to personally translate database content into any number of languages. Users can easily switch between languages and translate the user interface into new languages.
DHIS2 offers a number of mobile solutions, including SMS, plain HTML, and Java options for feature phones as well as a Web-based solution with offline support for smartphones. Clients can use their mobile phones for registering cases, events, and personal information tracking individuals, conducting surveys and collecting aggregate data. DHIS2's mobile solutions make it easier to use effectively, particularly in a number of low- and middle- income regions where DHIS2 is currently being deployed. DHIS2 Mobile can be deployed using the web interface to support an integrated HIS system usable by all levels of a health service or as a standalone mobile reporting system.
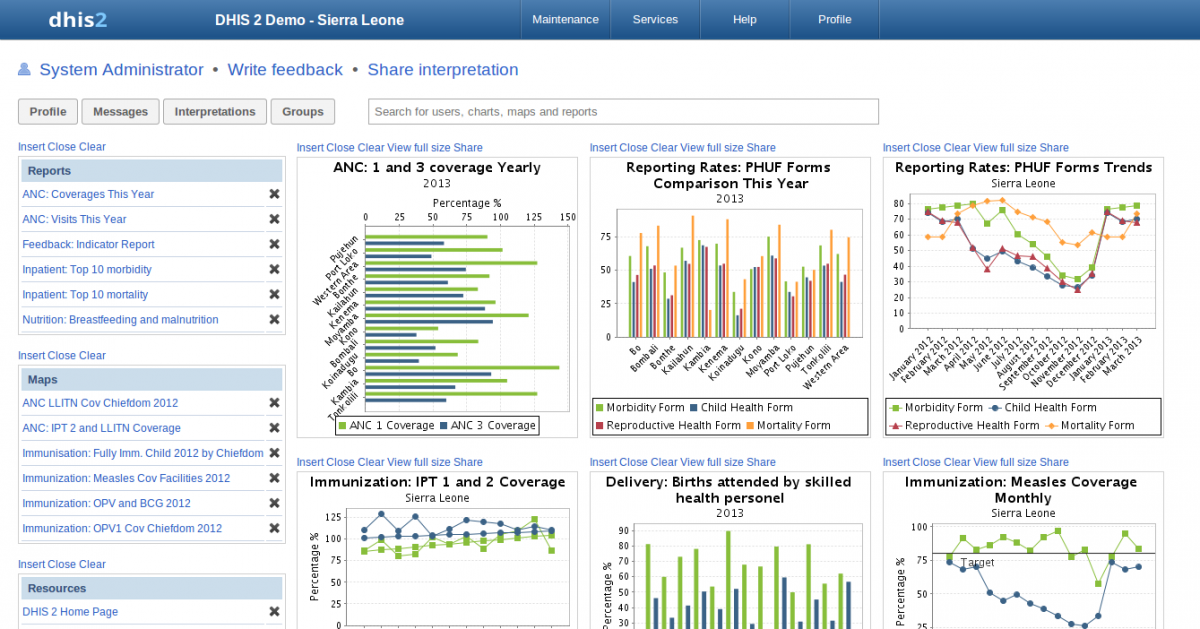 DHIS 2 dashboard screenshot
DHIS 2 dashboard screenshot
DHIS2 is a modular web-based software package built with free and open source Java frameworks and operates under a liberal BSD license. Clients can get DHIS2 as software-as-a-service, which includes system backups with safe storage at a remote server, SSL (HTTPS/encryption) use for data security, and stable, high-speed Internet connectivity. The service provider for DHIS2 software-as-a-service in the cloud is BAO Systems. DHIS2 is easily interoperable with third-party clients, including Web portals, Android apps, and other information systems. The source code of DHIS2 is hosted on GitHub.
DHIS 2 Academies
The DHIS2 Academies are offered in several regions throughout the year for anyone who has a strong interest in DHIS2. The goal is to build regional communities of DHIS2 users and experts. This way users and experts can share their experiences with DHIS2 deployments and their strategies for national implementations. You can learn more about these events here.
DHIS 2 Deployments:
 A CHW in Ghana measures the mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) of a 7-month-old on a home visit. The MUAC measurement is an potential indicator of malnutrition. (Credit - Direct Relief - CC-BY-NC-ND 2.0)Ghana has used DHIS2 nation-wide since April 2012 after delivering a national rollout of DHIS2 in just six months. Ghana Health Service has led this fully online deployment of DHIS2 and won The African Development Bank eHealth competition in 2013 for this implementation of the software. Hospitals in Ghana use the routine aggregate data collected monthly as well as the DHIS2 Tracker module with ICD-10 coded diagnosis to capture case-based data from inpatient admissions and deaths. This use of DHIS2 enables Ghana to collect more accurate morbidity and mortality statistics. You can read more about Ghana's implementation of DHIS2 here.
A CHW in Ghana measures the mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) of a 7-month-old on a home visit. The MUAC measurement is an potential indicator of malnutrition. (Credit - Direct Relief - CC-BY-NC-ND 2.0)Ghana has used DHIS2 nation-wide since April 2012 after delivering a national rollout of DHIS2 in just six months. Ghana Health Service has led this fully online deployment of DHIS2 and won The African Development Bank eHealth competition in 2013 for this implementation of the software. Hospitals in Ghana use the routine aggregate data collected monthly as well as the DHIS2 Tracker module with ICD-10 coded diagnosis to capture case-based data from inpatient admissions and deaths. This use of DHIS2 enables Ghana to collect more accurate morbidity and mortality statistics. You can read more about Ghana's implementation of DHIS2 here.
Kenya (hiskenya.org) was the first country in Sub-Saharan Africa to deploy a totally online health information system (HIS) powered by DHIS2, which was completed in September 2011. All the Kenyan districts and selected health facilities involved are connected to DHIS2 national server using Mobile Internet on computers. DHIS2 improves the Kenyan national health system's data analysis capabilities through an extensive facility survey that can now be conducted using the WHO SARA tool, which was customized through the DHIS2 Tracker. Kenya's online HIS self-registration for personal user accounts and the deployment of DHIS2 has increased the use of collaborative tools and encouraged more feedback from users. You can read more about Kenya's implementation of DHIS2 here.
 Medical sisters in Tanzania use a mobile phone while on a break of a Health Network meeting (Credit - Flickr user IICD - CC-BY-2.0)Tanzania (dhis.moh.go.tz) completed its nationwide rollout of DHIS2 in 2013. Use of DHIS2 has improved Tanzania's disease surveillance and response through its epidemiology unit's implementation of weekly eIDSR reporting that uses Mobile USSD to DHIS2. This implementation allows immediate outbreak and weekly summary data to be collected directly from all public, private, and faith-based organization (FBO) health facilities within the country. Another use of DHIS2, the Pay for Performance payout model into the DHIS2 National data warehouse, allows health service providers to fully monitor their performance and payments. You can read more about Tanzania's implementation of DHIS2 here.
Medical sisters in Tanzania use a mobile phone while on a break of a Health Network meeting (Credit - Flickr user IICD - CC-BY-2.0)Tanzania (dhis.moh.go.tz) completed its nationwide rollout of DHIS2 in 2013. Use of DHIS2 has improved Tanzania's disease surveillance and response through its epidemiology unit's implementation of weekly eIDSR reporting that uses Mobile USSD to DHIS2. This implementation allows immediate outbreak and weekly summary data to be collected directly from all public, private, and faith-based organization (FBO) health facilities within the country. Another use of DHIS2, the Pay for Performance payout model into the DHIS2 National data warehouse, allows health service providers to fully monitor their performance and payments. You can read more about Tanzania's implementation of DHIS2 here.
Uganda (hmis1.health.go.ug) took advantage of the rapidly improving mobile internet coverage in East Africa to deploy an online DHIS2 implementation in August 2012. Uganda is using new patient tracking capabilities in DHIS 2 to pilot an implementation called the Saving Mothers and Giving Life (SMGL). SMGL tracks mothers and children to improve the continuum of care. In the four pilot districts in Western Uganda, SMGL is collecting key indicators on maternal health using mobile phones. Uganda is also exploring different client platforms (such as smartphones, laptops, SMS messaging, and feature phones) for better reaching out to local health works and pregnant mothers. Through SMGL, Village Health Teams (VHTs) submit data directly to the online national DHIS2 system using SMS messaging, making data immediately available for analysis by all online users of all levers throughout Uganda. You can read more about Uganda's implementation of DHIS2 here.
 Malaria medication (Credit - Arne Hoel for World Bank - CC-BY-NC-ND 2.0)Zambia (hmis.dhis.co.zm) is currently using DHIS2 for data collection and Malaria eradication. The Zambia national HMIS platform's migration to DHIS2 supports data collection from health facilities across the country. DHIS2 has also been used successfully as a mobile reporting tool by Zambia's Malaria Control Program. This deployment allows community health workers (CHWs) enrolled in the malaria program to use mobile reporting to help track cases of malaria and the health interventions used to treat them. You can read more about Zambia's Malaria Control Program and its use of DHIS2 both here and here.
Malaria medication (Credit - Arne Hoel for World Bank - CC-BY-NC-ND 2.0)Zambia (hmis.dhis.co.zm) is currently using DHIS2 for data collection and Malaria eradication. The Zambia national HMIS platform's migration to DHIS2 supports data collection from health facilities across the country. DHIS2 has also been used successfully as a mobile reporting tool by Zambia's Malaria Control Program. This deployment allows community health workers (CHWs) enrolled in the malaria program to use mobile reporting to help track cases of malaria and the health interventions used to treat them. You can read more about Zambia's Malaria Control Program and its use of DHIS2 both here and here.
Countries using DHIS 2 are as follows:
Complete national implementation - Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Ghana, India (Bihar, Orissa, Maharashtra, Kerala, Punjab, Haryana, H Pradesh), Kenya, Liberia, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, The Gambia, Uganda, Zambia, Zanzibar, and Zimbabwe
Adoption via programs or partial national roll-out - Algeria, Bhutan, Burundi, Colombia, DRC, Laos, Malawi, Solomon Islands, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, and Vietnam
Pilot stage or early phase in roll-out - Afghanistan, Benin, Congo Brazzaville, Cote d'Ivoire, Guinea Bissau, Mexico, Myanmar, Namibia, Nepal, Niger, North Korea, Samoa, Senegal, South Sudan, Sudan, Timor Leste, and Vanuatu
Links to DHIS2 Stories in Open Health News
- DHIS2 - Transforming Health IT Standards in the Developing World (Part 2)
- Developing Nations Improving Health Communication Through the Use of DHIS2 (Part 1)
- “Write Code! Save Lives!” OpenMRS Meet in Malawi Shows the Way
- OpenMRS Conference in Uganda Redefines Global Health IT Collaboration
- Zambian Minister Says Open Source DHIS2 Is Vital for Healthcare
- How a Free Mobile App Fights Ebola and Other Global Epidemics
- Open Source App Takes on Ebola and Mental Health in Liberia
- OHNews 2013 Readers Choice: 'Open Source' Health IT Systems
- Linking Up to Use Health Information for Improving Health Outcomes
- A Ugandan mHealth Moratorium Is a Good Thing
- OpenMRS February 2013 Contributor of the Month: Roger Friedman
DHIS2 Social Media Links
Video: DHIS2 and modern health information systems in Malawi
Changelog:
- Updated 05/08/2018 with additional links and video feed.
- Updated 06/05/2018 with latest national deployment numbers. Added links to two additional articles.
- Tags:
- aggregate statistical data analysis
- aggregate statistical data collection
- aggregate statistical data management
- aggregate statistical data presentation
- aggregate statistical data validation
- Andriod apps
- BAO Systems
- BSD license
- community health workers (CHWs)
- data security
- database content translation
- DHIS 2 Academies
- DHIS 2 Mobile
- DHIS 2 National data warehouse
- DHIS 2 Tracker module
- District Health Information Software 2 (DHIS 2)
- East Africa
- eIDSR reporting
- European Union (EU)
- free and open source health management data platform
- free and open source software (FOSS)
- Ghana
- Ghana Health Service
- Github
- health data access
- Health Information Systems Program (HISP)
- HMIS platform's migration
- ICD-10 coded diagnosis
- integrated HIS system
- Java frameworks
- Kenya
- malaria eradication
- mobile reporting tool
- Mobile USSD
- modular web-based software package
- online health information system (HIS)
- open source
- patient health monitoring
- patient tracking
- Pay for Performance payout model
- safe storage
- Saving Mothers and Giving Life (SMGL)
- SMS messaging
- software-as-a-service
- SSL (HTTPS/encryption)
- sub-Saharan Africa
- Tanzania
- The African Development Bank eHealth competition
- Uganda
- Village Health Teams (VHTs)
- visualization features
- web portals
- WHO SARA tool
- Zambia
- Zambia's Malaria Control Program
- Login to post comments
